
Caffeine has several effects on the body, including increased alertness and improved mental and physical performance. Caffeine can also be produced by combining two molecules of uric acid. Total science geek? Check out the hyper-detailed description of the process. In summary, the chemical synthesis of caffeine is a process that involves combining two molecules of guanine and one molecule of adenine. Coffee brands using Swiss Water® Process communicate their decaffeination choice by use of the Swiss Water® Process seal or wordmark. How do you know how your coffee is decaffeinated? This is difficult unless the coffee package labeling identifies the method or process. And some leave behind more caffeine than you would think. Caffeine has a stimulating effect on the central nervous system, heart, blood vessels, and kidneys.It also acts as a mild diuretic.Caffeine’s potent stimulatory action makes it a valuable antidote to respiratory depression induced by drug overdose (e.g., from morphine or barbiturates). Most use chemical solvents such as methylene chloride or ethyl acetate to strip caffeine molecules from the green coffee bean. They antagonize or inhibit many of the adenosine receptors, like the A2A receptor. It is composed of purines structurally it is polar, and water soluble (Figure 1). However, it’s important to know that decaffeination methods vary. Caffeine (Trimethylxanthine) Caffeine, systematic name is 1,3,7-trimethylxanthine, is a xanthine derivative. People drink decaffeinated coffee for a variety of reasons. Still, it’s a bit more complicated than your average high school science class, so in short let’s just say you’re getting all the things you love about coffee without the caffeine. Our ecology-friendly water decaffeination process uses simple science to remove caffeine from green coffee beans. The SWISS WATER® Process is a taste-driven, 100% chemical-free decaffeination process that protects the unique origin characteristics and flavor of premium coffee beans. bold text-breaku0022u003En reseRvedn u003C/au003En u003Cem class.
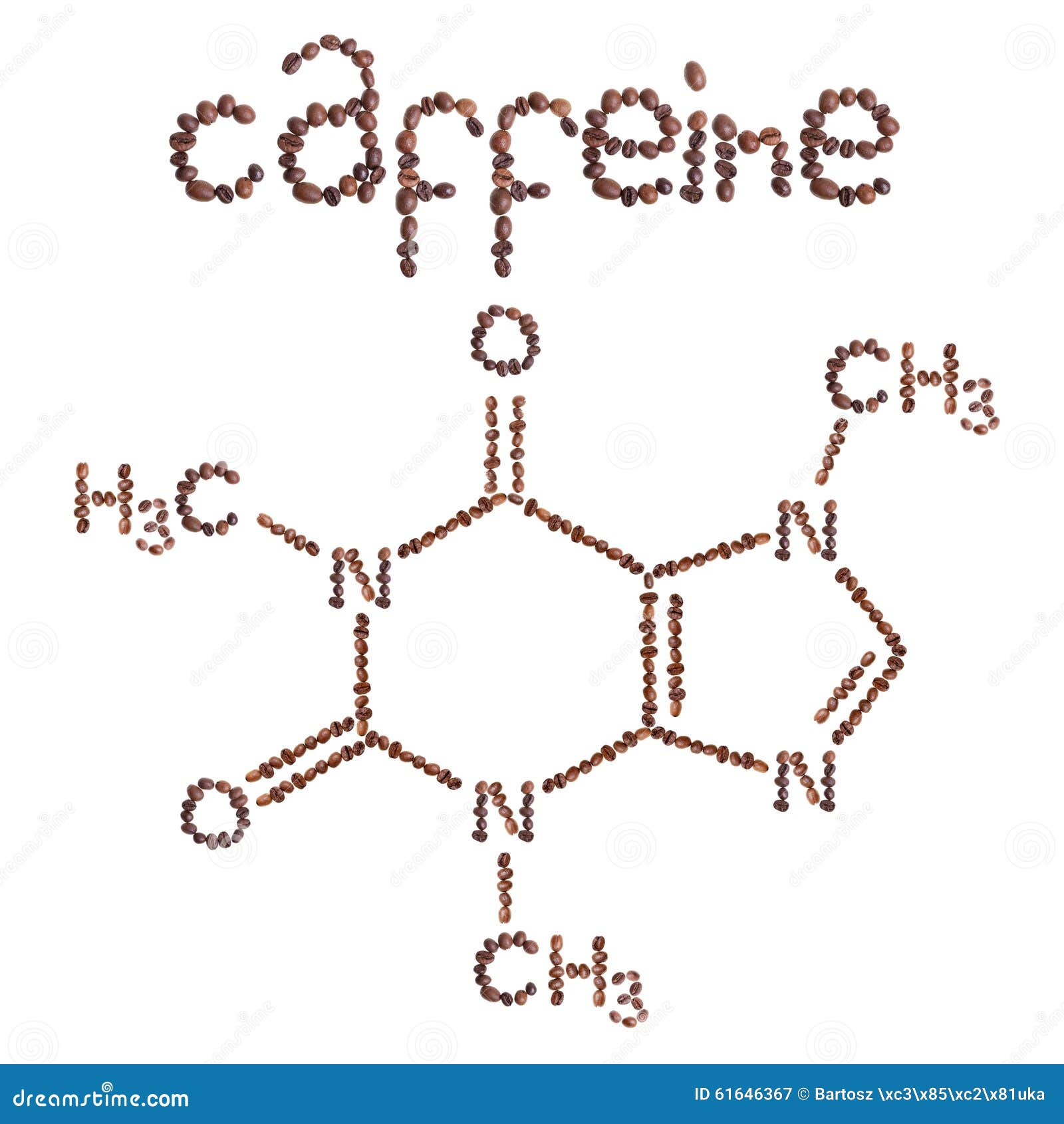
The chemical is also known as coffeine, theine, mateine, guaranine, or methyltheobromine. caffeine molecule.jpgVersionIdmdtJB0nesgDC8NG5Ku0022 /u003Ennu003C.

This maintains the bean’s distinctive origin and flavor characteristics. Caffeine (C 8 H 10 N 4 O 2) is the common name for trimethylxanthine (systematic name is 1,3,7-trimethylxanthine or 3,7-dihydro-1,3,7-trimethyl-1H-purine-2,6-dione). However, the proprietary Swiss Water® Process uses water from the pristine environment of the coast mountains of British Columbia, Canada to gently remove the caffeine until the coffee beans are 99.9% caffeine-free.

Most decaffeinated coffee uses chemical solvents such as methylene chloride or ethyl acetate to strip caffeine molecules from the green coffee bean. 100% chemical-free decaffeination process.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
